A frictionless and secure authentication for smart environments is highly needed.
Smart environments such as Smart-Cities, Smart-Buildings, Smart-Homes, Smart-Cars,
etc. are quickly replacing the traditional contexts in which people work, live,
and travel. Such technology-rich environments, however, must guarantee the same,
or even a higher level of safety and security to protect themselves and their citizen.
In this respect, authentication, that is the ability to verify the identity of users
while accessing services and infrastructure is well recognized to be the fundamental
security stepstone on which to build all other trust and security services. The
most important challenges while designing authentication technology for such environments
are the following:
Risk-driven security: the desired level of security should be adjusted dynamically
depending on context and application.
Frictionless: No extra effort should be required to the user just for the
purpose of authentication.
Applicable to any smart environment: it should be possible to customize the
authentication if applications or services require so.
Adaptable to any user: it must be universal, gender-independent, and multi-cultural.
Should accommodate aging, accident, and disabilities. Overall, it must be easy to
use and to understand
|
|
Step & Turn
|
Step & Turn is a novel bimodal behavioral biometric-based verification scheme
for physical access con- trol. In today’s rapidly evolving smart physical spaces,
frictionless and smooth interactions are emerging as critical usability requirements.
Such demands need to coexist with mandatory requirements like security. Step & Turn
addresses the fundamental limitations of the conventional physical access control
schemes, i.e., users having a specific knowledge or possessing a particular device
or token, to satisfy both usability and security requirements.
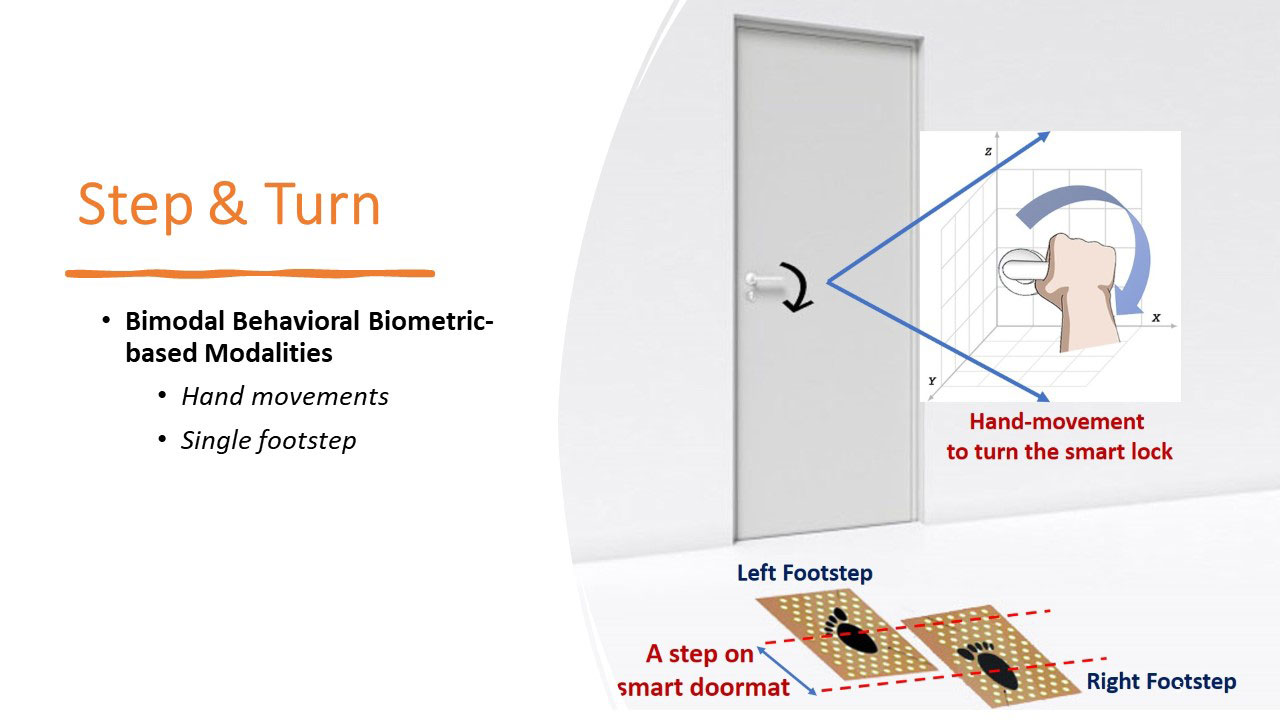
We design and develop a prototype of Step & Turn by exploiting two natural human
behaviors: single footstep and hand-movement to authenticate the users.
Step & turn - A novel bimodal behavioral biometric-based
user verification scheme for physical access control
S Gupta, Mouna Kacimi, B Crispo - Computers & Security, 2022
TopBack to wiki
|
|
DRIVERAUTH
|
On-demand ride services and the rideshare infrastructure primarily focus on the
minimization of travel time and cost. However, the safety of riders is overlooked
by service providers. For driver authentication, existing identity management methods
typically check the driving license, which can be easily stolen, forged, or misused.
Further, background checks are not performed at all; instead, social profiles and
peer reviews are used to foster trust, thereby compromising the safety and security
of riders. Moreover, the present mechanism seems ineffective in discontinuing a
malicious driver from offering the services.
DriverAuth — a fully transparent and easy-to-use authentication scheme for
drivers that is based on common behavioral biometric modalities, such as hand movements,
swipe action, and touch-strokes while the drivers interact with the dedicated smartphone-based
application for accepting the booking
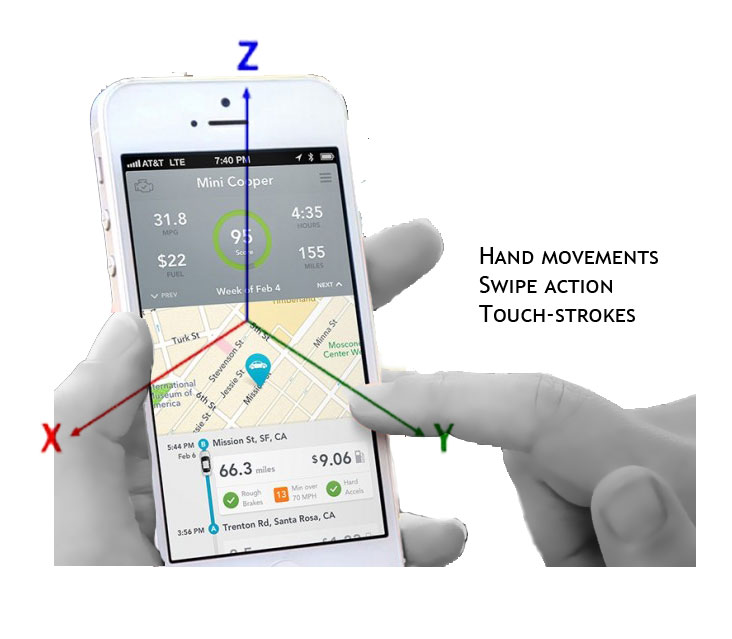
- This scheme exploits 3 modalities, i.e., hand movements, swipe action, and touch-strokes.
- This can be utilized for multi-user authentication in a client-server environment.
DriverAuth: Behavioral biometric-based driver authentication
mechanism for on-demand ride and ridesharing infrastructure
S Gupta, A Buriro, B Crispo - ICT Express, 2018
TopBack to wiki
|
|
SmartHandle
|
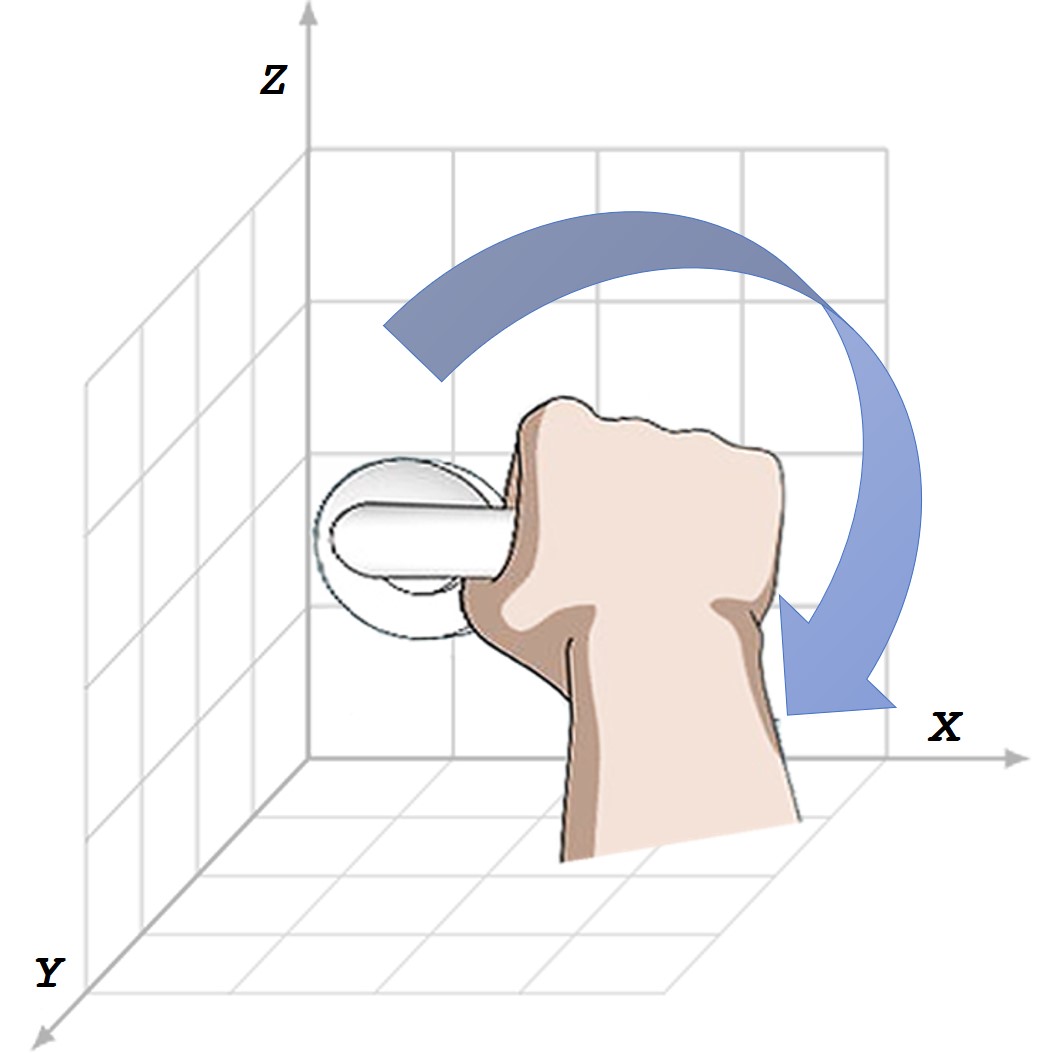
SmartHandle - a novel behavioral biometric-based transparent user authentication
scheme for smart locks that exploits users' hand-movement while they rotate the
door handle to unlock the door. More specifically, our solution models the user's
hand-movement in 3-dimensional space by fetching the X, Y, and Z coordinates from
3 sensors, namely, accelerometer, magnetometer, and gyroscope corresponding to the
hand-movement trajectory, to generate a user-identification-signature.
SmartHandle: A Novel Behavioral Biometric-based Authentication Scheme
for Smart Lock Systems
Gupta, Sandeep, Attaullah Buriro, and Bruno Crispo. "SmartHandle: A Novel Behavioral
Biometric-based Authentication Scheme for Smart Lock Systems." Proceedings of the
2019 3rd International Conference on Biometric Engineering and Applications. ACM,
2019.
TopBack to wiki
|
|
SNAPAUTH
|
SnapAuth is a motion-based unobtrusive behavioral biometric-based user authentication
solution - SnapAuth, for Android-based smartwatch. SnapAuth requires the user to
perform finger-snapping action, while wearing the smartwatch to perform the authentication.
SnapAuth profiles the arm-movements by collecting data from smartwatch's built-in
accelerometer and gyroscope sensors, while the user performs this action.
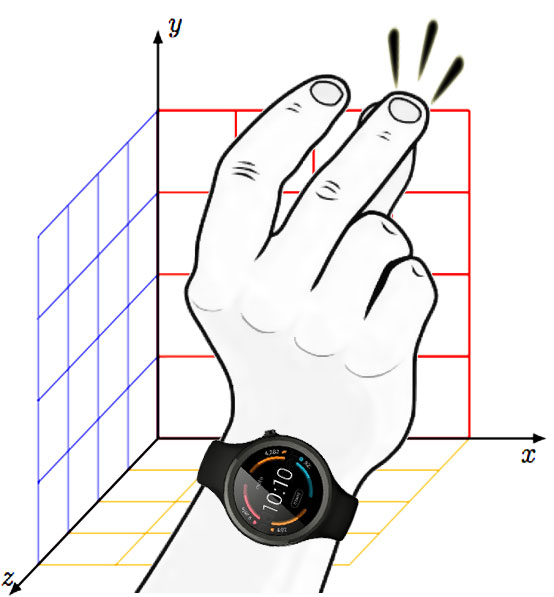
- This scheme exploits user's arm movements wearing a smartwatch.
- SnapAuth could be widely accepted by users as it utilizes the users' familiarity
with the very common finger-snapping action and users do not need to remember any
secret.
- This can also be utilized to authenticate the users in smart-homes.
We implemented and evaluated SnapAuth on Motorola Moto 3G smartwatch.
TopBack to wiki
|
|
ACTIVEAUTH
|
ACTIVEAUTH is a fully unobtrusive one-shot-cum-continuous user authentication scheme,
which in addition to authenticating the user at the login stage, continuously tracks
the user interactions and authenticate the user before security-sensitive operations
are performed. ACTIVEAUTH transparently monitors low-level events that correspond
to these sensitive operations and collects sensory readings to profile the phone
movements as a behavioral modality to profile the user.
TopBack to wiki
|
|
DIALERAUTH
|
DIALERAUTH exploits the way a smartphone user taps or enters any text-independent
10-digit number (replicating the dialing process) and the hand's micro-movements
while entering the numbers on the touchscreen of a smartphone.
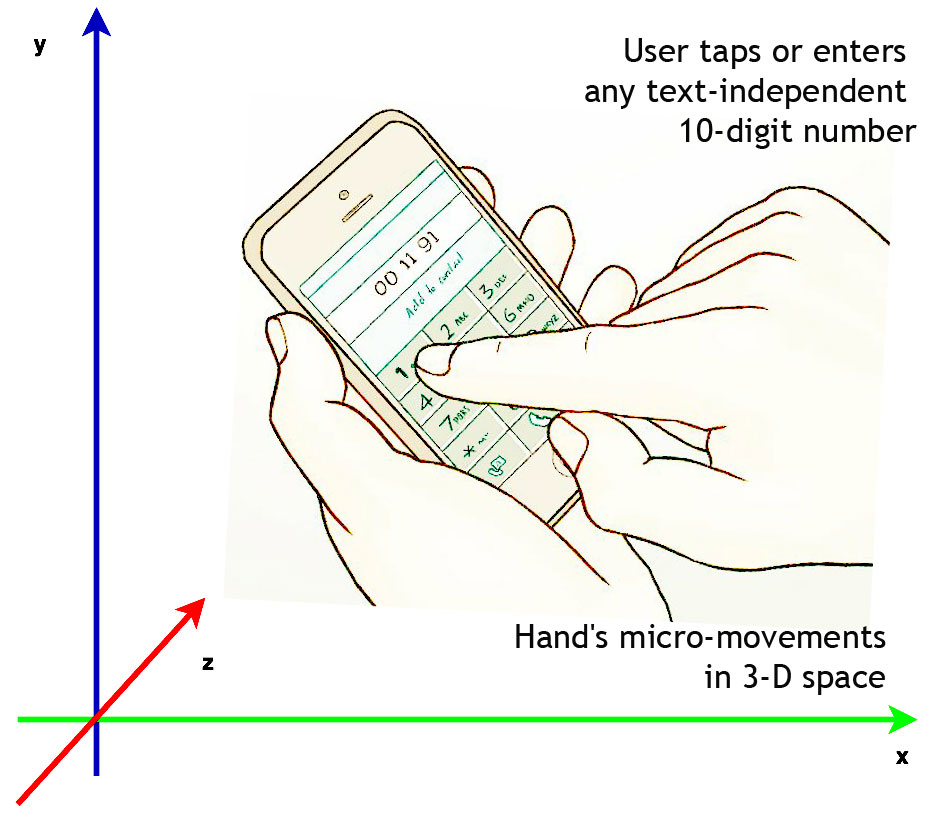
- DIALERAUTH authenticates a user on the basis of timing differences in the entered
10-digit taps and user's hand micro-movements recorded by using using accelerometer
and gyroscope sensors.
- DIALERAUTH provides enhanced security by leveraging the transparent and unobservable
layer and increases the usability and acceptability by utilizing the users' familiarity
with the dialing process and the flexibility of choosing any combination of 10-digit
number.
- This scheme can be utilized to authenticate users on their smartphone.
DIALERAUTH: A Motion-assisted Touch-based Smartphone
User Authentication Scheme
Attaullah Buriro, Bruno Crispo, Sandeep Gupta, Filippo Del Frari. In: CODASPY '18
Proceedings of the 8th ACM Conference on Data and Application Security and Privacy
Pages 267-276
Top Back to wiki
|
|
Touchstroke
|
Touchstroke is bi-modal biometric authentication solution, which leverages users'
hand movements while they hold their smartphones, and touch-typing timing differences
when they enter a text-dependent 4-digit PIN/password.
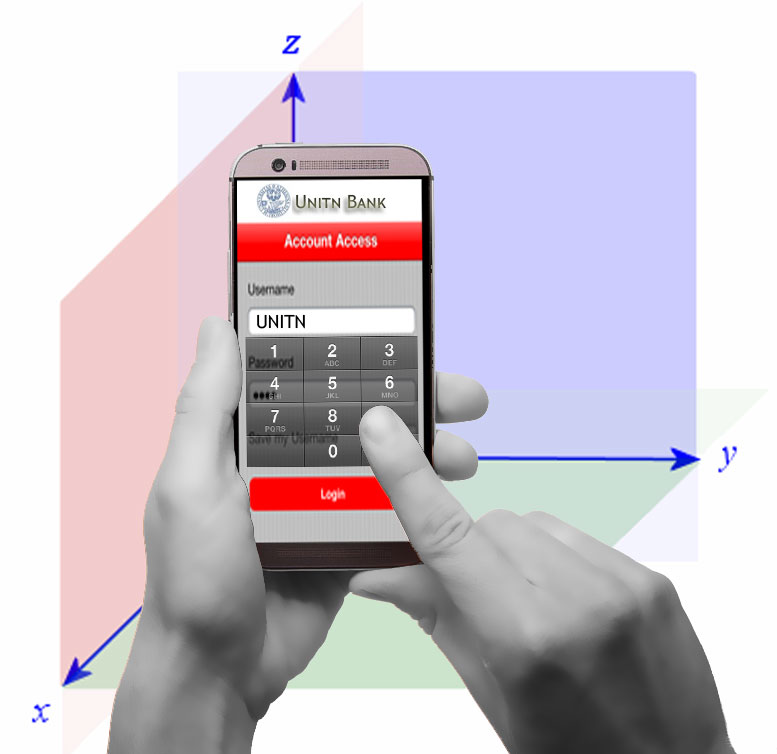
The scheme can be deployed as single user authentication, i.e., user authentication
on smartphones, as well as multiple user authentication (implemented using client-server
architecture), i.e., user authentication for sensitive application like banking
apps.
Touchstroke: Smartphone User Authentication Based
on Touch-Typing Biometrics
Buriro A., Crispo B., Del Frari F., Wrona K. (2015). In: Murino V., Puppo E., Sona
D., Cristani M., Sansone C. (eds) New Trends in Image Analysis and Processing --
ICIAP 2015 Workshops. ICIAP 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9281. Springer,
Cham
Evaluation of motion-based touch-typing biometrics in online financial environments
Buriro, At., Gupta, Sa. & Crispo, Br., (2017). In: Brömme, Ar., Busch, Ch., Dantcheva,
An., Rathgeb, Ch. & Uhl, An. (Hrsg.), BIOSIG 2017. Gesellschaft für Informatik,
Bonn. (S. 219-226).
TopBack to wiki
|
|
ANSWERAUTH
|
AnswerAuth- a user-friendly behavioral biometric-based user authentication mechanism,
which is based on two very common human actions, i.e., how the user slide-to-unlock
her smartphone (sliding) and and how she moves her smartphone towards her ear (phone-pickup).

AnswerAuth: A bimodal behavioral biometric-based
user authentication scheme for smartphones
Buriro, Attaullah, Bruno Crispo, and Mauro Conti. "AnswerAuth: A bimodal behavioral
biometric-based user authentication scheme for smartphones." Journal of information
security and applications 44 (2019): 89-103.
TopBack to wiki
|
|
ITSME
|
ITSME: a multi-modal behavioural biometric that uses features collected while the
user slide-unlocks the smartphone to answer a call. In particular, we use the slide
swipe, the arm movement in bringing the phone close to the ear and voice recognition
to implement our behaviour biometric.
- This is a trimodal authentication using arm movements, swipe action, and voice on
smartphones.
- This can be utilized for single user authentication.
Itsme: Multi-modal and unobtrusive behavioural user
authentication for smartphones
Buriro A., Crispo B., Del Frari F., Klardie J., Wrona K. (2016). In: Stajano F.,
Mjølsnes S.F., Jenkinson G., Thorsheim P. (eds) Technology and Practice of Passwords.
PASSWORDS 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9551. Springer, Cham
TopBack to wiki
|
|
Hold and Sign
|
Hold and Sign is a bi-modal behavioral biometric solution for user authentication.
The proposed mechanism takes into account micro-movements of a phone and movements
of user's finger during writing or signing on the touchscreen. More specifically,
it profiles a user based on how she holds the phone and based on the characteristics
of the points being pressed on the touchscreen, and not the produced signature image.
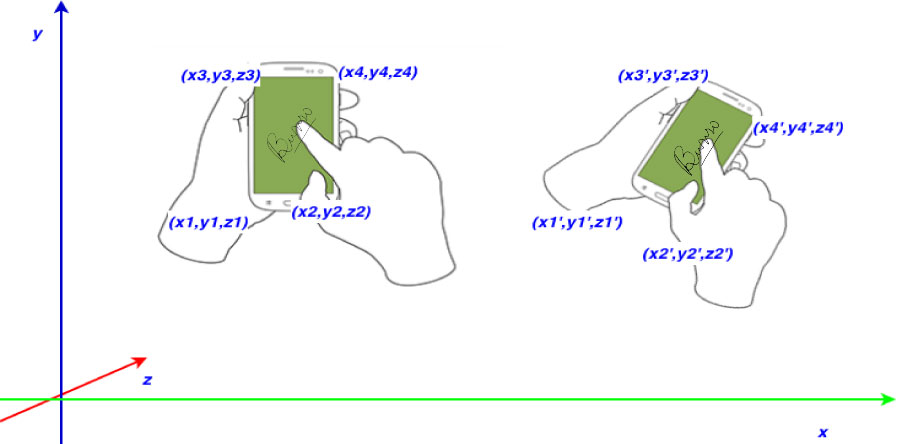
- This scheme exploits 2 modalities, i.e., hand movements, and users signature pattern.
- This can be utilized for authenticating a user in banking scenario.
Hold and Sign: A Novel Behavioral Biometrics for Smartphone User
Authentication
A Buriro, B Crispo, F Delfrari, K Wrona - Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW),
2016 IEEE, 2016
Please hold on: Unobtrusive user authentication using smartphone's
built-in sensors.
Buriro, Attaullah, Bruno Crispo, and Yury Zhauniarovich; Identity, Security and
Behavior Analysis (ISBA), 2017 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2017.
TopBack to wiki
|